The Sun, a luminous ball of hot plasma at the center of our solar system, is a celestial marvel that has fascinated and sustained life on Earth for billions of years. It serves as the primary source of light and energy, driving the dynamics of our planetary system. In this blog post, we will delve into the intriguing characteristics of the Sun, exploring its structure, role in the solar system, and the profound impact it has on life on Earth.
The Sun’s Structure
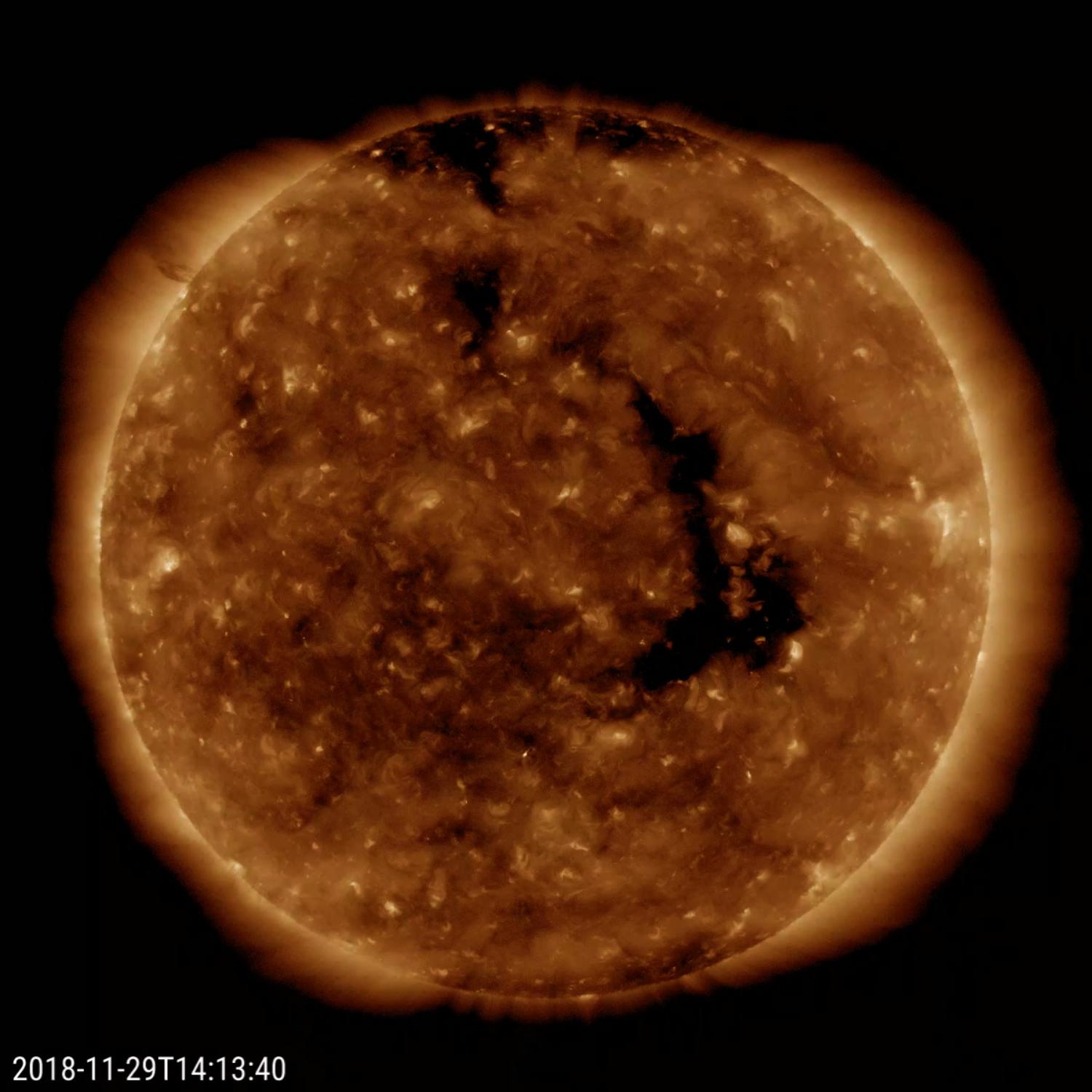
The Sun is a massive, nearly perfect sphere composed primarily of hydrogen (about 74% by mass) and helium (about 24%). Its immense gravitational pull, caused by the concentration of such enormous mass, gives rise to an internal pressure and temperature that enable nuclear fusion in its core. This process releases an unimaginable amount of energy in the form of light and heat, which radiates out into space.
The Sun’s interior is divided into several layers, each with distinct properties. The core, where temperatures reach about 15 million degrees Celsius, is the site of nuclear fusion, primarily converting hydrogen into helium. Surrounding the core are the radiative and convective zones, where energy generated in the core gradually makes its way to the Sun’s surface. The outermost layer, the solar atmosphere, consists of the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona, each contributing to the Sun’s unique appearance and behavior.
The Solar Cycle
The Sun experiences an 11-year solar cycle, marked by fluctuations in its magnetic activity. This cycle involves the waxing and waning of sunspots—temporary phenomena caused by the Sun’s magnetic field. During periods of high solar activity, sunspots are abundant, and solar flares and coronal mass ejections become more frequent. Conversely, during periods of low solar activity, the Sun’s surface appears relatively calm.
The impact of the solar cycle is not limited to the Sun alone. It influences space weather, affecting communication systems, satellites, and even power grids on Earth. Understanding these solar variations is crucial for mitigating potential risks associated with space weather events.
Solar Energy and Light
The Sun’s most significant contribution to our daily lives is the energy it provides. Through the process of nuclear fusion, the Sun emits light and heat, creating the perfect conditions for life on Earth. The sunlight reaching our planet sustains ecosystems, drives weather patterns, and supports photosynthesis—the fundamental process that enables plants to convert sunlight into energy.
Solar energy, harnessed through solar panels, has become a key player in the quest for sustainable and renewable energy sources. The Sun’s power, captured by photovoltaic cells, is converted into electricity, offering a clean and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy sources. As technology advances, our reliance on solar energy is likely to grow, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Eclipses: Celestial Spectacles
Eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events, occur when the Earth, Moon, and Sun align in specific configurations. Two types of eclipses—solar and lunar—provide breathtaking displays of the Sun’s influence on the cosmic dance of our celestial neighbors.
During a solar eclipse, the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, casting a shadow on our planet. This temporary blockage of sunlight creates a surreal experience as day turns into night for a brief moment. Observers in the path of totality witness the solar corona, the Sun’s outer atmosphere, glowing like a delicate halo around the obscured solar disk.
The Importance of Studying the Sun
Scientists and astronomers continuously study the Sun to unravel its mysteries and better understand the fundamental processes that govern its behavior. Space missions, such as NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter, provide invaluable data that enhances our comprehension of solar dynamics, magnetic fields, and their impact on the solar system.
Studying the Sun also contributes to our knowledge of other stars in the universe. As a G-type main-sequence star, the Sun serves as a benchmark for understanding stellar evolution and the potential habitability of exoplanets orbiting other stars.
Conclusion
The Sun, with its captivating beauty and life-sustaining energy, holds a central role in the cosmic ballet of our solar system. From the intricate layers of its interior to the mesmerizing phenomena observable during solar eclipses, the Sun continues to captivate our curiosity and drive scientific exploration. As we harness solar energy for a sustainable future and deepen our understanding of the Sun’s complex dynamics, we unveil the profound influence this celestial powerhouse exerts on our existence and the broader cosmos.
Leave a Reply